Two new studies add to the evidence that social isolation is a substantial risk factor for dementia in community-dwelling older adults, new research shows.
The research also identifies technology as an effective way to intervene.
Collectively, the studies don’t establish a direct cause and effect between dementia and social isolation, defined as lack of social contact and interactions with people on a regular basis. But, the researchers say, the studies strengthen observations that such isolation increases the risk of dementia, and suggest that relatively simple efforts to increase social support of older adults—such as texting and use of email—may reduce that risk.
In the United States, an estimated 1 in 4 people over age 65 experience social isolation, according to the National Institute on Aging.
“Social connections matter for our cognitive health, and it is potentially easily modifiable for older adults without the use of medication,” says Thomas Cudjoe, assistant professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and senior author of both of the new studies.
The first study, published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, used data collected on a group of 5,022 Medicare beneficiaries for a long-term study known as the National Health and Aging Trends, which began in 2011. All participants were 65 or older, and were asked to complete an annual two-hour, in-person interview to assess cognitive function, health status, and overall well-being.
At the initial interview, 23% of the 5,022 participants were socially isolated and showed no signs of dementia. However, by the end of this nine-year study, 21% of the total sample of participants had developed dementia. The researchers concluded that risk of developing dementia over nine years was 27% higher among socially isolated older adults compared with older adults who were not socially isolated.
“Socially isolated older adults have smaller social networks, live alone, and have limited participation in social activities,” says Alison Huang, senior research associate at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. “One possible explanation is that having fewer opportunities to socialize with others decreases cognitive engagement as well, potentially contributing to increased risk of dementia.”
Interventions to reduce that risk are possible, according to results of the second study, published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. Specifically, researchers found the use of communications technology such as telephone and email lowered the risk for social isolation.
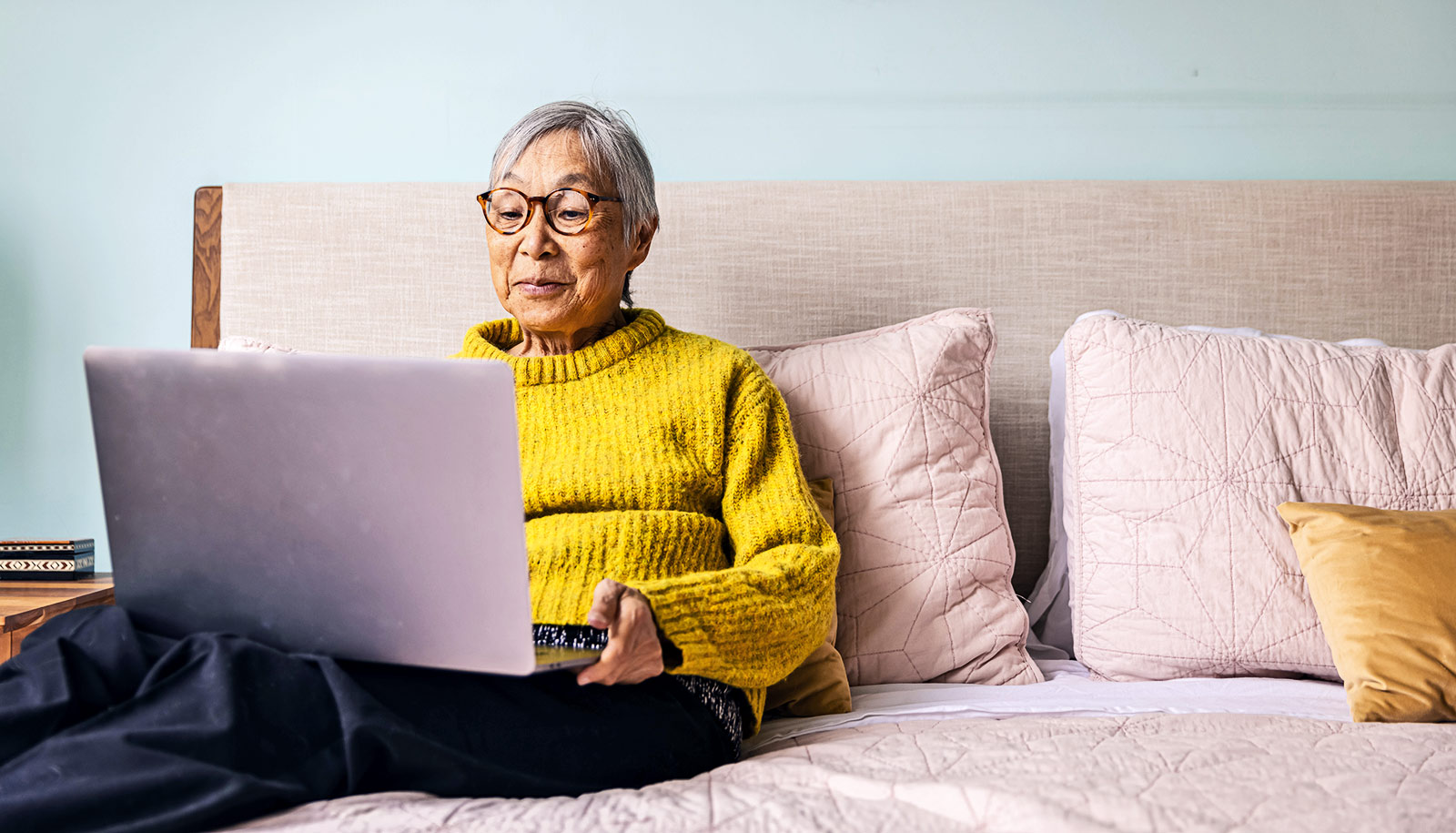
Researchers for the second study used data from participants in the same National Health and Aging Trends study, and found that more than 70% of people age 65 and up who were not socially isolated at their initial appointment had a working cellphone and/or computer, and regularly used email or texting to initiate and respond to others.
Over the four-year research period for this second study, older adults who had access to such technology consistently showed a 31% lower risk for social isolation than the rest of the cohort.
“Basic communications technology is a great tool to combat social isolation,” says Mfon Umoh, a postdoctoral fellow in geriatric medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “This study shows that access and use of simple technologies are important factors that protect older adults against social isolation, which is associated with significant health risks. This is encouraging because it means simple interventions may be meaningful.”
Social isolation has gained significant attention in the past decade, especially due to restrictions implemented for the COVID-19 pandemic, but more work needs to be done to identify at-risk populations and create tools for providers and caregivers to minimize risk, the researchers say. Future research in this area should focus on increased risks based on biological sex, physical limitations, race, and income level.
Funding for the studies came from the Caryl & George Bernstein Human Aging Project, the Johns Hopkins University Center for Innovative Medicine, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institute on Aging, the Secunda Family Foundation, the Patient-Centered Care for Older Adults with Multiple Chronic Conditions, and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Source: Johns Hopkins University